Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Last updated
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Last updated
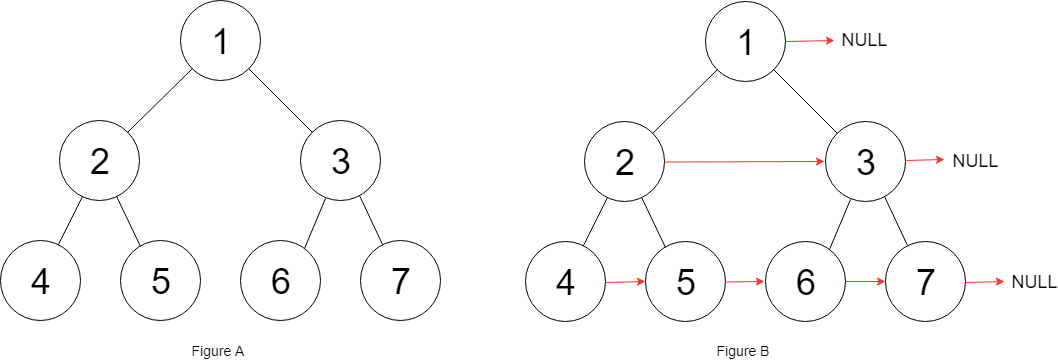
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.def connect(self, root):
while root and root.left:
next = root.left
while root:
root.left.next = root.right
root.right.next = root.next and root.next.left
root = root.next
root = next